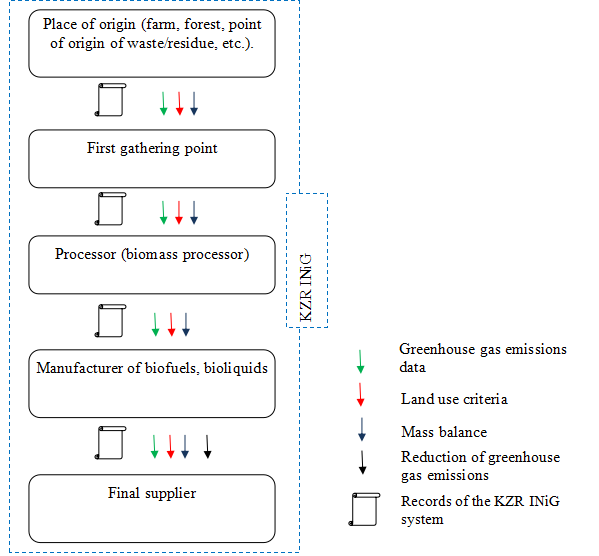
Certification pathway: biofuels and bioliquids
Biofuels means liquid fuel for transport produced from biomass.
Bioliquids means liquid fuel used for energy purposes other than transport, including electricity and heating and cooling, produced from biomass.
Agricultural raw materials for biofuel production
e.g. corn, wheat, sugar beet, rapeseed, sunflower
Land status verification, GHG emissions for the cultivation stage
Residues as raw materials for biofuel production
Always zero greenhouse gas emissions at the cultivation stage
Bio-components can be counted twice if the residue is listed in Annex IX of Directive 2018/2001. Land criteria do not apply to industrial residues.
For agricultural residues, verification of soil quality management is required.
Ethanol:
Ethanol is typically accounted for in volume units, but mass balance should be conducted in mass units. For mass balance accounting, quantities expressed in volume units must be converted to mass units – tons.
Biodiesel:
Produced through the transesterification of oils with methanol. Methanol can be sourced from fossil or renewable sources. Regardless, 100% of biodiesel is always counted as biofuel. However, if methanol comes from fossil sources, the appropriate GHG emission factor (from Regulation 2022/996) must be applied.
Greenhouse gas emissions arising from the cultivation of rapeseed in the Poland NUTS2 regions (grams CO2eq/kilograms rapeseed harvested on dry matter basis)
| NUTS 2 region according to Regulation (EC) No 1059/2003 | Total |
| L51 DOLNOŚLĄSKI | 560 |
| PL61 KUJAWSKO-POMORSKI | 616 |
| PL81 LUBELSKI | 606 |
| PL43 LUBUSKI | 561 |
| PL71 ŁÓDZKI | 591 |
| PL21 MAŁOPOLSKI | 563 |
| PL92 MAZOWIECKI | 541 |
| PL52 OPOLSKI | 603 |
| PL82 PODKARPACKI | 593 |
| PL84 PODLASKI | 604 |
| PL63 POMORSKI | 614 |
| PL22 ŚLĄSKI | 555 |
| PL72 ŚWIĘTOKRZYSKI | 499 |
| PL62 WARMIŃSKO-MAZURSKI | 580 |
| PL91 WARSZAWSKI-STOŁECZNY | 579 |
| PL41 WIELKOPOLSKI | 625 |
Greenhouse gas emissions arising from the cultivation of maize in the Poland NUTS2 regions (grams CO2eq/kilograms maize harvested on dry matter basis
| NUTS 2 region according to Regulation (EC) No 1059/2003 | Total |
| PL51 DOLNOŚLĄSKI | 343 |
| PL61 KUJAWSKO-POMORSKI | 282 |
| PL81 LUBELSKI | 273 |
| PL43 LUBUSKI | 295 |
| PL71 ŁÓDZKI | 265 |
| PL21 MAŁOPOLSKI | 242 |
| PL92 MAZOWIECKI | 292 |
| PL52 OPOLSKI | 261 |
| PL82 PODKARPACKI | 262 |
| PL84 PODLASKI | 298 |
| PL63 POMORSKI | 247 |
| PL22 ŚLĄSKI | 254 |
| PL72 ŚWIĘTOKRZYSKI | 251 |
| PL62 WARMIŃSKO-MAZURSKI | 231 |
| PL91 WARSZAWSKI-STOŁECZNY | 316 |
| PL41 WIELKOPOLSKI | 282 |
| PL42 ZACHODNIOPOMORSKI | 274 |